The world of skincare is undergoing a paradigm shift as the allure and desire for applying natural rather than synthetic ingredients onto one’s skin takes center stage. In this article, we will explore the field of ethnobotany and medicinal plants (i.e., Mother Nature’s ingredients), unearthing the hidden treasures of nature’s healing properties. Discover how indigenous wisdom, scientific research, and a passion for healthier looking and feeling skin converge in this holistic approach to skincare.
Imagine, for a moment, a lush forest filled with all the best natural ingredients Mother Nature has to offer, where ancient traditions and cutting-edge biotechnology meet. This is the stage on which ethnobotany and medicinal plants play their roles. Here, nature’s secrets are waiting to be revealed and accessed, promising a path to healthy, radiant skin and overall well-being.
In a polluted world filled with synthetic or petrochemical ingredients and complex forever chemicals, the desire for skincare products made from natural ingredients is undeniable. The idea of harnessing the power of Mother Nature’s offerings to enhance our skincare rituals is both appealing and refreshing. But where does this journey begin and what is ethnobotany?

WHAT IS ETHNOBOTANY? [1]
Ethnobotany is a multidisciplinary field that delves into the fascinating and intricate relationship between people and plants. It’s the art of understanding how cultures have traditionally used plants for various purposes, including medicine. This is where science and tradition intersect and our search for knowledge and understanding begins.
Think of ethnobotany as a grand library, filled with books that document the knowledge and secrets passed down over generations. Each “book” is a different plant, and its pages are filled with the secrets of its uses. This treasure-trove of knowledge reveals how people from different corners of the world have for years harnessed the healing properties of plants.
Ethnobotany goes beyond just the scientific study of plants. It serves as a bridge between cultures and their indigenous knowledge. Indigenous communities have been the keepers of this botanical wisdom for millenia, preserving it for future generations. It is this connection to culture and tradition that makes the field of ethnobotany so rich and fascinating!
WHAT IS ETHNOBOTANICAL MEDICINE? [2]
Ethnobotanical medicine is concerned with the cultural interpretations of health and disease, which also addresses the traditional healthcare-seeking process and healing practices. It takes the knowledge gathered through ethnobotany and applies it to address health concerns. It is also the practical application of the medicinal power of plants to improve human health and well-being, i.e., the transformation of plants into remedies.
Imagine ethnobotanical medicine as a kind of laboratory where the ingredients used are plants, and the scientists working with these ingredients are skilled healers capable of unlocking their chemical and biological powers. Each plant possesses a unique health-benefiting property and together they create a natural healing remedy
The collective knowledge embodied by ethnobotany and ethnobotanical medicine is nothing short of an encyclopedia of nature. It contains the accumulated wisdom of centuries, detailing the remarkable properties and uses of Mother Nature’s ingredients. This knowledge is like a beautiful garden, with each plant representing a page in the encyclopedia. By exploring this garden, we discover plants that can heal, rejuvenate, protect, and enhance our well-being.
WHAT IS MEDICINAL ETHNOBOTANY? [2]
Medicinal ethnobotany (i.e. plant biotechnology) transcends folklore and tradition by providing a scientific justification for the use of plants in medicine. It is the scientific validation of what indigenous peoples have known for generations, using modern scientific methods and technologies to confirm the efficacy of these remedies.
Think of medicinal ethnobotany as a laboratory equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and researchers in lab coats. Their mission is to evaluate and scrutinise plant-based remedies, dissecting their chemical compositions and properties to uncover the mechanisms of action behind their healing properties.
The world of modern medicine has not ignored ethnobotany’s hidden healing treasures. Numerous drugs and treatments have their roots in traditional plant-based remedies including aspirin which comes from willow bark; digitalis, which comes from foxglove; quinine, which comes from the cinchona tree; and morphine, which comes (albeit indirectly) from the opium poppy. These discoveries serve as a testament to the validity and effectiveness of ethnobotanical knowledge.
Picture modern medicine as being a giant puzzle, with each piece representing a plant-derived active compound. As we assemble the puzzle, it reveals a clear picture of how Mother Nature’s pharmacy can contribute to and improve our health and wellbeing. Plant biotechnology is the tool and methodology by which we discover and optimize the remedy.
PLANT-BASED ACTIVES FROM IRELAND [3]
Ah Ireland, with its lush landscapes and unique flora, it offers a rich source of plant-based actives for creating a natural skincare routine. The emerald isle’s natural botanical treasures are a testament to the power of indigenous plants. Examples of Irish medicinal plants and their uses include:
- Meadowsweet: because it contains salicylic acid, it has long been used for its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. It can be used topically to help soothe skin conditions like rashes and other irritations.
- Bog Myrtle: its antiseptic properties make it ideal for facilitating wound healing. It is used topically for treating cuts and skin infections based on its ability to clean and protect wounds.
- Nettle: a versatile plant with anti-inflammatory properties. It is used topically to help treat and soothe eczema/atopic dermatitis flare-ups.
- Yarrow: valued for its astringent and anti-inflammatory properties. It is traditionally used for promoting wound healing.
- Lady’s Bedstraw: a plant whose actives have traditionally been used to treat eczema and psoriasis due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
PLANT-BASED ACTIVES FROM CHILE [4]
Chile is home to a diverse collection of native plants traditionally used to treat various skin conditions, especially if crafting a “natural face skincare” regimen is your goal. Examples include:
- Matico: this plant’s leaves contain active ingredients with both antimicrobial and astringent properties. It has traditionally been used to promote wound healing and help alleviate symptoms associated with various skin conditions.
- Maqui: its berries are rich in potent antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins (polyphenols), which help neutralize oxidative stress-causing free radicals present in the skin. Topical application of this botanical active has been shown to support skin health and slow down skin’s aging process.
- Murtilla: also known as Chilean guava, is also rich in antioxidants, especially Vitamin C. It can be used topically to rejuvenate skin, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and promote a healthy complexion.
- Boldo: because its leaves have antimicrobial properties it can be used topically as a natural remedy for skin infections. It can also help soothe skin irritation and promote wound healing.
- Copaiba: this resin contains anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial compounds. Hence, it can be applied topically to alleviate skin conditions like acne and psoriasis by reducing redness and inflammation.
PLANT-BASED ACTIVES FROM AYURVEDA [5]
Ayurveda, India’s ancient system of medicine, offers a wealth of knowledge on plant-based skincare actives. It’s like an ancient sacred text filled with age-old wisdom on the harmony of body, mind, and spirit. When its secrets are applied to the field of skincare, it's like taking a journey to the heart of India where beauty and well-being intersect. Examples include:
- Neem: known for its strong antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, it is used to treat a variety of skin conditions including acne, eczema, psoriasis, and fungal infections. Neem can also help purify the skin, thereby alleviating itching and redness.
- Turmeric: containing curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compound, it is used to treat skin conditions like acne, wounds, and inflammatory skin disorders. It is used to help reduce inflammation and promote skin healing.
- Sandalwood: with both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, it’s used to treat skin conditions like acne, rashes, and blemishes. It is used for its ability to help reduce redness and inflammation while promoting clearer looking skin.
- Tulsi: also known as “holy basil” possesses antibacterial and anti-inflammatory to help purify the skin and soothe irritation. This plant is used in Ayurveda to treat acne, skin infections, and reduce inflammation.
NATURAL, PLANT-BASED SKINCARE ROUTINES: THE CODEX BIOTECH WAY
The transition to a natural skincare routine is a part of the “clean beauty” revolution. It represents a shift towards cleaner, more sustainable practices that prioritize the health of both your skin and the planet. Creating a customized, effective natural face skincare routine cannot, however, ignore science. Biotechnology is all about selecting the “right” plant-based active ingredients (down to the plant stem cells) that can effectively address your skin’s unique needs and preferences.
Fortunately for you, Codex Labs has done much of the heavy lifting when it comes to vetting the plethora of knowledge, wisdom, and information contained in Mother Nature’s arsenal of medicinal plants. Our R&D team spent years studying, evaluating, and working with biotech-derived botanical active ingredients to formulate products that have been clinically proven to do what Mother Nature says they can do!
Our BIA® COLLECTION is a line of products whose foundation is built on plant-based actives derived from Irish medicinal plants and improved upon (no offense Mother Nature) through the use of modern day biotech. The result is a skincare line specifically formulated for those with dry, sensitive and/or compromised skin in dire need of hydration and the ability to lock in moisture.
The technology developed by our team of scientists for this uber-hydrating line was deemed so innovative that a United States patent was granted to recognize this achievement. Our award-winning BIA® HYDRATING SKIN SUPERFOOD moisturizer, with its patented BiaComplex® technology quenches parched skin while sealing in moisture leaving your skin soothed, happy, and flake free. Oh, and by the way, it has also been given a thumbs up by the National Eczema Association!
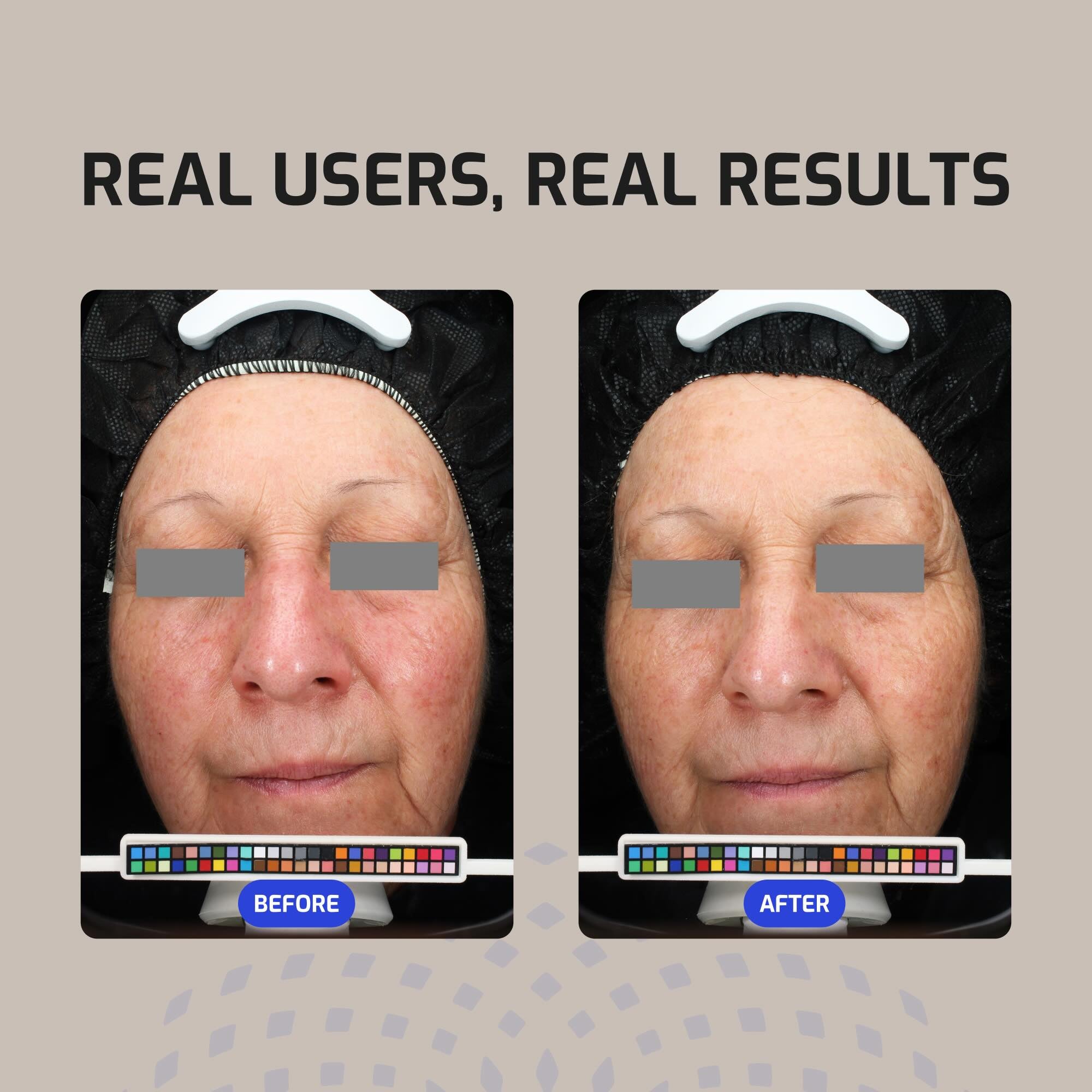
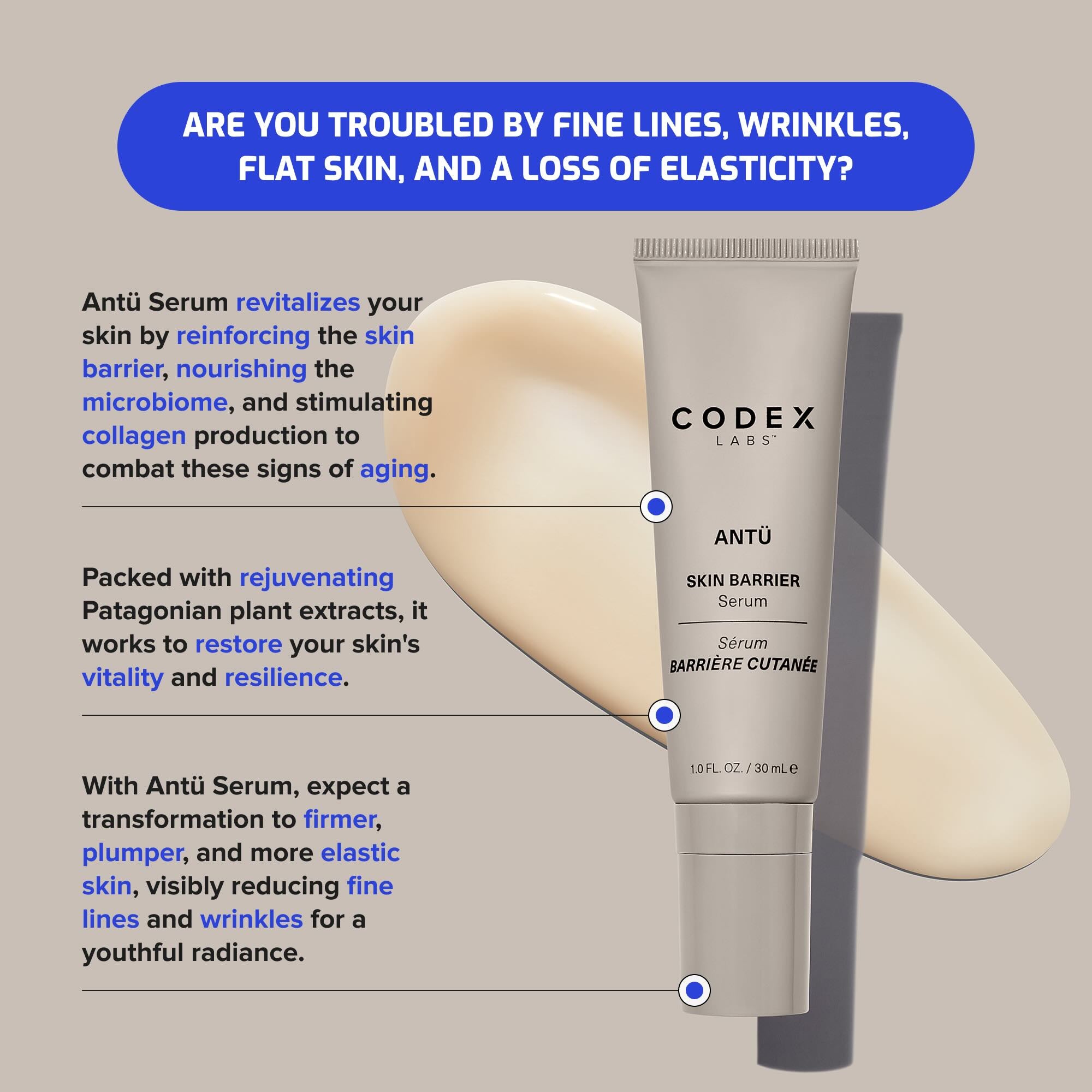
The ANTU® COLLECTION is based on Patagonian plant actives wild-harvested from Chile due to their ability to neutralize free radicals caused by sunlight and air pollution. These free radicals, if left unchecked, cause the skin barrier to become inflamed and experience oxidative stress leading to the premature aging of skin referred to as “inflammaging”. The Chilean botanical actives selected by Codex’s scientists, because they contain highly potent antioxidants (anthocyanins and polyphenols), effectively scavenge and neutralize free radicals in skin. Once neutralized these radicals lose their ability to trigger inflammation and promote premature skin aging (inflammaging).
Here too, the technology developed by our team of scientists for this skin barrier rejuvenating, free radical neutralizing line was deemed so innovative and efficacious that it too was deserving of a granted United States patent. Our award-winning ANTU® SKIN BARRIER SERUM, with its patented AntuComplex® technology jam-packed with potent antioxidants and biotech-derived humectants not only rejuvenates and protects your skin barrier from free radicals to keep it functioning at a high level, it also helps inhibit premature aging caused by inflammation.
Lastly, there is the SHAANT® COLLECTION and its line of Ayurveda-based products for treating oily, inflamed, acne-prone skin. Chock-full of Ayurvedic medicinal plant actives and biotech-derived marine algae meant to reduce the appearance of redness, calm and soothe inflamed skin, and manage the production of inflammation-causing sebum (oil) by the skin, this line of products highlights Mother Nature’s toolkit of acne- and inflammation-fighting Ayurvedic botanical actives.
Once again (I hope they don’t ask for a raise), our crackerjack team of skilled scientists developed a technology for which, yet another patent was granted. Referred to as ShaantComplex®, it embodies an innovative combination of specific botanical actives that synergistically work together to specifically address acne. For those suffering from this all-too-common skin condition who would rather roll with Mother Nature’s medicinal ingredients rather than the synthetic one created by chemical companies, this is the clinically proven “natural” option you’ve been waiting for!
CONCLUSION
Ethnobotany has the power to bridge your current skincare regimen to. By embracing the knowledge and wisdom of traditional plant-based actives, and applying state-of-the-art biotech science, you can unlock the potential of nature’s healing properties for your skin. The fusion of ethnobotany, ethnobotanical medicine, biotechnology and the wisdom of indigenous cultures enables those individuals interested in avoiding synthetic ingredients to, instead, develop a natural skincare routine that represents an integrative approach to healthy skin. This type of natural face skincare regimen not only enhances the health and appearance of your skin, but also honours the planet. Never bet against Mother Nature!
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4967429/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9526633/#:~:text=Ethnobotany%20is%20the%20study%20of,other%20economic%20applications%20%5B1%5D.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0102695X14000076
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10051824/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5871155/